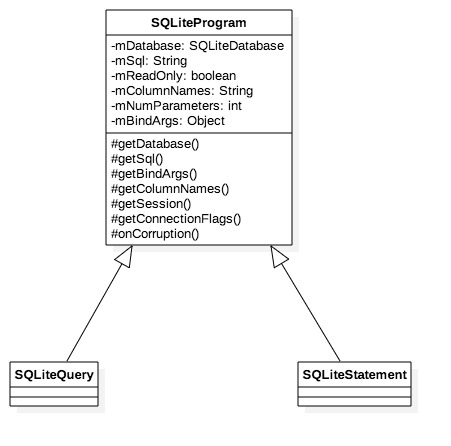
本篇只局限于Framework层源码,源码版本为Android 8.0 SQLiteProgram SQLite CRUD操作的执行离不开一个非常关键的类 —— SQLiteProgram 。正是通过SQLiteProgram,SQLiteDatabase完成了操作API 到具体执行(SQLiteSession) 的解耦。 SQLiteProgram有两个实现子类,SQLiteQuery 和 SQLiteStatement 。
SQLiteQuery: 负责Query的执行转发处理。SQLiteStatement: 负责Insert/Update/Delete的执行转发。
通过 getSession() SQLiteSession 中。在 SQLiteSession 中,SQLiteConnection 将CRUD绑定到native去执行。
Query SQLiteDatabase 中Query相关的API,穿透之后到了rawQueryWithFactory() 中,并交由SQLiteDirectCursorDriver() 执行Query。
SQLiteDirectCursorDriver.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public Cursor query(CursorFactory factory, String[] selectionArgs) { final SQLiteQuery query = new SQLiteQuery(mDatabase, mSql, mCancellationSignal); final Cursor cursor; try { query.bindAllArgsAsStrings(selectionArgs); if (factory == null) { cursor = new SQLiteCursor(this, mEditTable, query); } else { cursor = factory.newCursor(mDatabase, this, mEditTable, query); } } catch (RuntimeException ex) { query.close(); throw ex; } mQuery = query; return cursor; }
可以看到,上层调用query()经过层层调用,最后只是直接返回了一个初始化的 Cursor对象 ,这个 Cursor对象的缓冲区是空的,这个时候还没有执行真正的 数据库query() 。 SQLiteDatabase qeury() 的作用是创建了一个Cursor,并不立即往数据库执行query()语句。
什么时候执行query语句的呢? 做过SQLiteDatabase开发的App工程师一定对Cursor的moveToFirst() 方法很熟悉。在该方法中,会调用到getCount() 来统计Cursor中row的数目,如果当前统计的row数目为-1 (NO_COUNT ),则会调用fillWindow() 来执行 query查询,并将查询的结果填充到缓冲区CursorWindow 当中。后面对Cursor执行的getString()、getInt() 之类的方法就仅仅是读取出CursorWindow中的内容罢了。执行query语句查询的时刻便是涉及调用到 getCount() 方法,同时当前CursorWindow不可用时(mCount = -1 ) 。
填充缓冲区CursorWindow CursorWindow的填充工作都交由SQLiteQuery (SQLiteDirectCursorDriver执行query()一开始创建) 来完成,并被转发到SQLiteSession 中去执行。SQLiteSession 是由SQLiteDatabase根据所获取到的SQLiteConnectionPool 对象创建的一种用来操作SQLiteConnection的Client包装类。executeForCursorWindow()
SQLiteSession.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public int executeForCursorWindow(String sql, Object[] bindArgs, CursorWindow window, int startPos, int requiredPos, boolean countAllRows, int connectionFlags, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal) { if (sql == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("sql must not be null."); } if (window == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("window must not be null."); } //执行特殊的SQL语句,主要是跟Transaction相关的begin、commit、 end.... if (executeSpecial(sql, bindArgs, connectionFlags, cancellationSignal)) { window.clear(); return 0; } //如果mConnection为空,则从ConnectionPool acquire 一个;添加引用计数 acquireConnection(sql, connectionFlags, cancellationSignal); // might throw try { //转发到native去执行。 return mConnection.executeForCursorWindow(sql, bindArgs, window, startPos, requiredPos, countAllRows, cancellationSignal); // might throw } finally { releaseConnection(); // might throw } }
Pang、Pang、Pang ,最后又去到了Native里…
Insert insert 操作在SQLiteDatabase中,经过SQLiteStatement 的转接,最终依旧交给了SQLiteSession 中去执行。
SQLiteDatabase.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public long insertWithOnConflict(String table, String nullColumnHack, ContentValues initialValues, int conflictAlgorithm) { acquireReference(); try { ...... SQLiteStatement statement = new SQLiteStatement(this, sql.toString(), bindArgs); try { return statement.executeInsert(); } finally { statement.close(); } } finally { releaseReference(); } }
同Query操作差不多,在SQLiteSession 中先检查Transaction相关的语句去执行,然后获取一个数据库连接,由数据库连接去操作native的insert操作
SQLiteSession.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public long executeForLastInsertedRowId(String sql, Object[] bindArgs, int connectionFlags, CancellationSignal cancellationSignal) { if (sql == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("sql must not be null."); } if (executeSpecial(sql, bindArgs, connectionFlags, cancellationSignal)) { return 0; } //获取数据库连接 acquireConnection(sql, connectionFlags, cancellationSignal); // might throw try { //转发到native去执行 return mConnection.executeForLastInsertedRowId(sql, bindArgs, cancellationSignal); // might throw } finally { releaseConnection(); // might throw } }
Update & Delete Update 和 Delete 的流程极其相似,都是通过SQLiteStatement 的 executeUpdateDelete() 方法并最终转发到SQLiteConnection的 executeForChangedRowCount() 中去执行,在 executeForChangedRowCount() 中执行native方法。
SQLiteDatabase.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public int updateWithOnConflict(String table, ContentValues values, String whereClause, String[] whereArgs, int conflictAlgorithm) { if (values == null || values.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty values"); } acquireReference(); try { ...... SQLiteStatement statement = new SQLiteStatement(this, sql.toString(), bindArgs); try { return statement.executeUpdateDelete(); } finally { statement.close(); } } finally { releaseReference(); } } public int delete(String table, String whereClause, String[] whereArgs) { acquireReference(); try { SQLiteStatement statement = new SQLiteStatement(this, "DELETE FROM " + table + (!TextUtils.isEmpty(whereClause) ? " WHERE " + whereClause : ""), whereArgs); try { return statement.executeUpdateDelete(); } finally { statement.close(); } } finally { releaseReference(); } }